Following the mining of bitcoin’s genesis block in 2009, the world witnessed a revolution that very few understood. Actually, the advent of the bitcoin network, ignited a global shift similar to what the internet did in the early 90s of the past century. Most people’s reactions were negative, when they were first introduced to bitcoin, thanks to a misguided perception that the new currency was namely used in money laundering, or for buying drugs and pornographic material. On the other hand, some realized that the cryptography, mathematics, philosophy and system design behind bitcoin’s network were invented by a genius, or a team of geniuses, who had a deep understanding of the problems of the global financial system.
The Four Ds of the Digital Economy:
The 21st century was marked by the emergence of a novel digital economy, that is pillared on 4 Ds; Digitalization, Democratization, Disintermediation and Decentralization). While incumbents are struggling to hold on to what they have and are comfortable with, mindset is far more pivotal than skillset. This exhibit of inertia urged many economy leaders to be more or less forceful throughout their public speeches, to impose change.
Paradigm Switch Throughout the Production Function:
The fourth industrial revolution, which was catalyzed by digital innovations, has totally rewritten the whole production function while focusing on a different group of factors. In conventional economics, the main production factors are labor, land and capital. Nevertheless, the advent of digital devices, the world wide web, and the ability to reign data, has transformed the backbone of global economy and business. The new global economy relies more on time, data and capital raising capabilities. Let’s delve into these factors together:
Along the supply chain of online business and e-commerce, land and geolocation are of minimal importance, given the fact that the computational server they utilize occupies a relatively small area and can be hosted far away on the digital cloud. Labor can be substituted by data technology that serves customers efficiently, and if this is insufficient, robots and artificial intelligences (AI) can even take over complex jobs such as factory jobs.
Equipment and machinery, which workers utilize to efficiently produce goods represent parts of a business’s capital within the context of the traditional economy. With the combination of computing power, data technology, 3D printing, and other novel hardware and software, along with the long (7 or more) years before profitability can be achieved, the capability of raising funds transposes physical equipment’s acquisition, as business’s new essential. As such, any new business that is not sufficiently investing in computing power, data technology and the ability to entice new funds will be almost irrelevant in the near future.
LASIC Principles:
As the global economy began relying on a digital-base; with Big Data, AI, 3D printing, IoT and blockchains, academic studies were conducted to determine factors that are common to successful businesses. In their 2015 study, Lee and Teo explored the features of successful companies e.g. M-PESA, Ant Financial and Fidor Bank. The three companies feature the LASIC characteristics; Low Margin, Asset Light, Scalable, Innovative and Compliance (Look at the below figure).
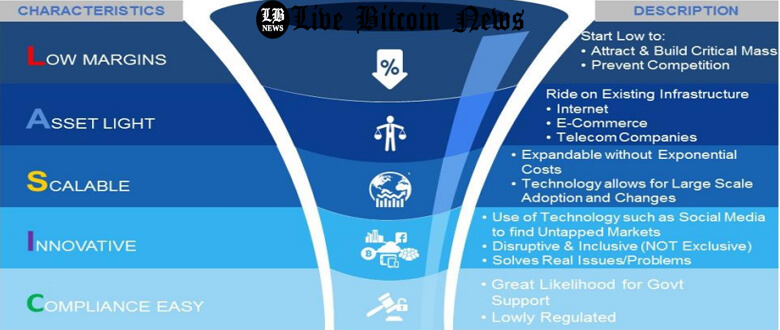
Enticing low margin critical mass and preventing competition are crucial for these forms of internet based businesses. Businesses that incur significant capital expenditure are characterized by high depreciation costs. Nonetheless, reliance on existing frameworks, e.g. the internet, telecom companies and e-commerce networks operate via a light balance sheet. Accordingly, such companies are capable of scaling with minimal costs to meet the adopters’ changing demands.
Also, these companies’ business models are extremely innovative throughout the process of searching for untapped and underserved markets via a disruptive, inclusive technology that is capable of addressing the customers’ main concerns. Furthermore, most of these companies operate within the conext of a compliance friendly ecosystem, which is mostly unregulated, when governmental frameworks are considered.
In analyzing these models that are consistent with the LASIC principles, researchers emphasized that to design a Hinternet, decentralization is not a necessity. A Hinternet represents a digital, or a virtual, space that has a big population of sticky customers, e,g, Alibaba’s e-commerce network. Alipay and Grab are associated with huge LASIC Hinternets that promote selling a wide array of products to those sticky customers. A blockchain is not necessary for designing a Hinternet business, yet to promote sustained growth, Decentralization i.e., the last D, is needed and as such, may involve the blockchain technology.
Decentralization creates a high barrier, so that oligopoly and monopoly market frameworks cannot be easily established. An extremely large sized Hinternet can lead to systematic risks and thus, increases the possibility of being broken up by regulations. With decentralization in action, regulation and legislation may play minimal roles, yet the goal of democratization of technology, information and services is achieved. Price discovery within the context of a decentralized ecosystem is a pivotal issue, yet it is beyond the scope of this article.


