The blockchain technology has opened the door for a myriad of financial solutions that are just beginning to unfold. A group of researchers have just published a paper that presents an E-commerce Blockchain Consensus Mechanism (EBCM) that can aid in building a secure, public, credible, autonomous network for e-commerce related transactions.
EBCM is based on the same blockchain data structure as that of bitcoin, yet a modification has been proposed to promote higher efficiency levels. Credibility is guaranteed via the introduction of validation blockchain, and building a two-layered blockchain, known as “peer blockchain”, in order to facilitate real time, high throughput transactions. The contributions of this research can be broken down to two elements:
- EBCM is put forward which does not rely on tokenization and computing power, yet it offers a level of credibility and security that is similar to that of Nakamoto’s consensus.
- EBCM offers real time, high throughput transactions and forking of the blockchain can never occur.
An overview of the E-commerce transaction network:
The e-commerce transaction network (BCTN) utilizes EBCM that relies on P2P (an illustration of the network can be shown in the below figure). BCTN utilizes e-commerce trading center, which is ideally convenient for auditing by the supervision department. It is comprised of a verification network (VENT) and a group of multiple peers.
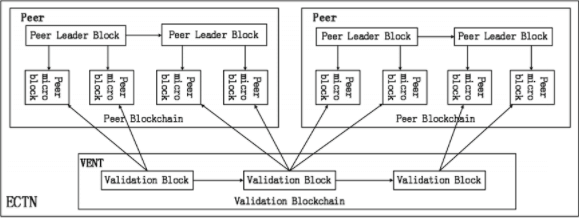
Peer:
A peer can be thought of as a center for e-commerce trading, or as a form of logistics platform, e.g. Tmall. Each peer across the network has an identity authentication, which includes a public key, which is responsible for encryption of messages, and a private key, which is responsible for digitally signing the blocks. It can maximize the security of messages and as such, blocks can never be forged.
Verification Network (VENT):
The verification network is comprised of peers who have verification rights. VENT’s main function is to guarantee that all peers’ micro-blocks cannot be tampered with. Verification rights mean that special peers, known as verification peers (VPs), have the right to build validation blocks.
The Peer Blockchain:
The peer blockchain is created in the form of a two layer blockchain to promote real time, high throughput transactions. It includes peer micro blocks and peer leader blocks. The header of the peer micro block includes the following:
- A signature which is essential for the identification of the creator of a block.
- The time of creation of a block in GMT format.
- The data’s hash value, which is based on the SHA256 algorithm to guarantee irreversibility and uniqueness.
The header of the peer leader block contains all the aforementioned elements, but along with the previous block’s hash value which can link peer leader blocks together to form a blockchain.
Validation Blockchain:
The validation blockchain records all headers of peer micro blocks to guarantee that each and every peer micro block cannot be tampered with. The link value of the current block, as well as the proceeding block, can link all verification blocks together into a blockchain.
The micro block’s size is fixed and the time needed for its creation is less than a predetermined threshold value TM, which promotes real time transactions. The number of block headers, which are recorded onto the verification block and the peer leader block is also fixed.